Partitioned Global Address Space
What is Partitioned Global Address Space (PGAS)?¶
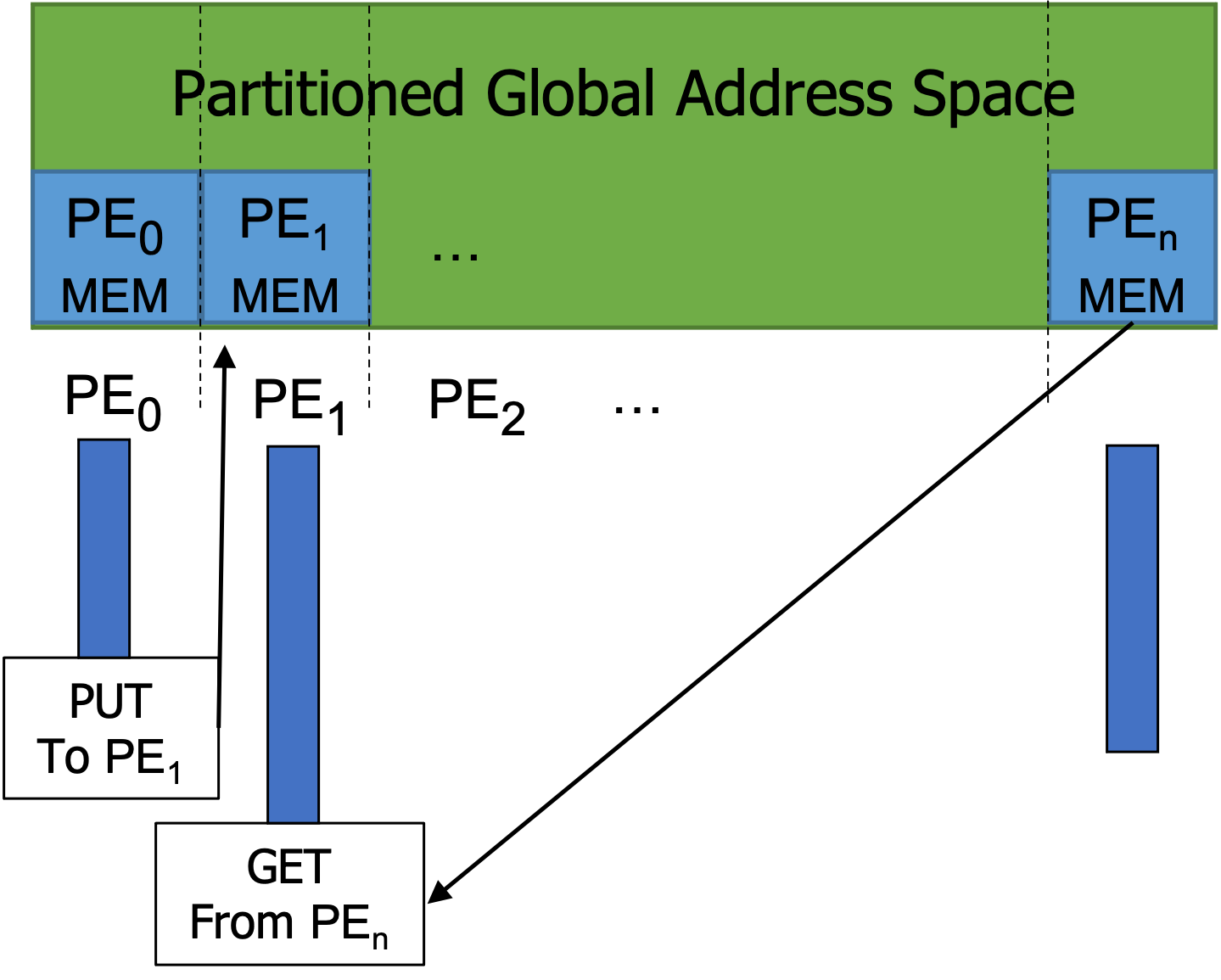
The PGAS (pronounced p-gas) is a programming model which gives the user the illusion of shared memory on distributed systems. As the name implies, you can imagine that there is a single shared global address space consisting of logical portions, each portion of which is local to each processing element (PE). Typically, many PGAS languages/libraries offer point-to-point one-sided communication, where the user can use 1) put routine to write data to a remote (non-local) location, 2) get routine to read data from a remote location, whereas MPI requires two-sided communication.
Note
While recent versions of MPI supports one-sided communications, that is not as simple as what PGAS languages/libraries offer.
Examples of PGAS languages/libraries¶
- X10
- Chapel
- Unified Parallel C (UPC)
- Co-Array Fortran (CAF)
- OpenSHMEM